YouTube Deep Summary
YouTube Deep Summary
Extract content that makes a tangible impact on your life
🤖 AI-Generated Summary:
Enhancing DNA Sequence Design with AI and Bioinformatics Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide
Hi everyone! I’m Dr. Mahil Kulak, Chief Scientific Officer at Exonic. Today, I want to walk you through an exciting and slightly advanced process of optimizing DNA sequences using AI models combined with bioinformatics tools. This approach not only improves the DNA sequence scores but also ensures their biological realism, which is crucial for successful lab experiments.
Step 1: Generating and Optimizing Random DNA Sequences
We start by generating random DNA sequences and assigning them an initial score using our AI model. The goal is to improve this score, which reflects the quality or functionality of the sequence according to our criteria.
- Initial random generation: This provides a baseline score.
- Optimization: Using the optimizer module, we connect it to the random generator and run the model to enhance the sequence scores.
- Outcome: We aim for a score above 15, and often the AI model can generate sequences with scores as high as 19, which is excellent.
Step 2: Ensuring Biological Realism with DNA Bird Embeddings
AI models can sometimes produce extreme or unrealistic sequences. To address this, we use the DNA Bird tool, which embeds our sequences into a real biological context by comparing them to actual DNA data from Molinos et al.
- The tool finds the closest neighbors in the embedding space, which represent biologically plausible sequences.
- This step helps us ground our AI-generated sequences in reality.
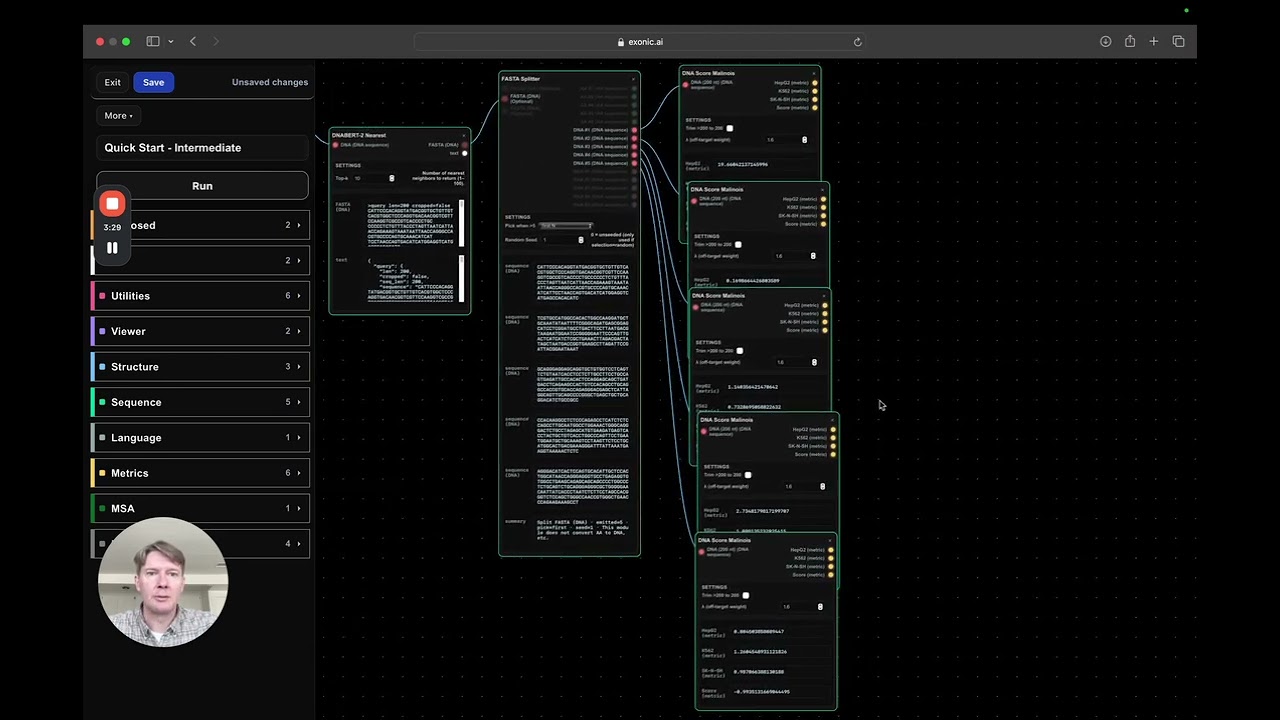
Step 3: Splitting and Scoring Sequences for Detailed Analysis
To analyze the generated sequences in detail, we use the DNA Fast Splitter utility:
- It splits the output into the original sequence plus the top four closest neighbors found by DNA Bird.
- We then score each sequence individually using multiple DNA Score modules, allowing us to compare how each variant performs.
Step 4: Evaluating Transcription Factor Binding with JASPAR
Biological activity of DNA sequences often depends on transcription factors (TFs) binding to them. To evaluate this:
- We use the JASPAR matrix tool, which ranks transcription factors based on their binding affinity to our sequence.
- The highest-ranking TFs indicate where and how strongly proteins might bind to the DNA, affecting its activity inside cells.
Step 5: Refining Sequences by Modulating Transcription Factor Sites
Using insights from JASPAR:
- We identify key TF binding sites within the sequence using the DNA Viewer tool.
- By adding or modifying these sites (for example, adding copies of a TF binding motif), we can enhance the sequence’s activity scores.
- This manual adjustment helps us balance scores such as the K562 activity, aiming to keep undesirable off-target effects low (below 1).
Step 6: Finalizing and Submitting the Optimized Sequence
Once satisfied with the improvements:
- We copy the refined DNA sequence into the DNA design panel.
- Submit the sequence for further testing or synthesis.
- The system confirms the validity of the sequence and displays updated scores.
Key Takeaways
- Combining AI with real biological data embeddings ensures that optimized DNA sequences are both high-scoring and biologically plausible.
- Utilizing tools like DNA Fast Splitter and JASPAR provides detailed insights into sequence functionality and protein-DNA interactions.
- Manual refinement of transcription factor binding sites can further improve sequence performance and reduce potential off-target effects.
- This integrated approach accelerates the design of functional DNA sequences ready for wet lab testing.
I hope this walkthrough gives you a clear understanding of how advanced AI-driven tools can be harnessed for DNA sequence design. Best of luck with your designs and experiments!
Dr. Mahil Kulak
Chief Scientific Officer, Exonic